- Statement of the Chairman of the Management Board
- Federal Grid Company General Information
- Corporate Governance
- Internal Control System
- The Risk Management System
- Understanding of Corporate Social Responsibility and Sustainable Development
- Human Resources Management
- Managing of the Economic Impact
-
Anti-corruption and Prevention of Conflict of Interests System
- JSC Federal Grid Company`s Anti-Corruption Policy
- Program for Prevention of Corruption and Settlement of Conflict of Interests in Federal Grid Company for 2012-2014
- Implementation of Anti-Corruption Policy and Program for Anti-corruption and Settlement of Conflict of Interests in Federal Grid Company in 2012
- 2013 Plans
- Environmental Impact Management
- Stakeholders Relations
-
APPENDICES
- The UNEG Reliability Provisions
- Innovative Development of the UNEG
- GRI Guidelines Indicators (G 3.1 and the Industry Protocol for Electric Power Industry), Reflected in the Report
- A Report on the Fulfillment of the 2012 CSR Plans and Obligations of JSC FGC UES (Draft)
- A Table of Stakeholders’ Suggestions Pertaining to the Disclosure of Information in the Report, Voiced at the Dialogue on 05.04.2013 and at the Public Hearings on 26.04.2013
- A List of Natural Areas in Preferential Protection (NAPP) Accessible for JSC FGC UES for the Purposes of Operation
- Independent Assurance of Social Reporting
- Glossary and Abbreviations
Internal Control System
Objectives of the internal control system
The Internal Control System (ICS) was formed in 2008. Its main goals are improving the Company’s performance and reliability of the financial statements of the Company, strengthening investor confidence in the Company and its management bodies, preserving assets and the efficient use of the Company’s resources.
On August 2, 2012, the Company’s Board of Directors approved new Regulations on the Internal Control System. Particular attention is focused on the preventive control of the Company’s activities by means of risk management. This task is performed by means of early identification, assessment and management of risks that threaten the Company’s business operations and reputation, the health of workers, the environment and property interests of shareholders and investors.
Currently, the internal control system provides:
- — compliance with applicable laws and internal policies, regulations and procedures of the Company;
- — achievement of the strategic goals of development, the implementation of financial and business plans;
- — prevention, timely detection of and response to threats to the Company’s activities;
- — Prevention, detection and elimination of violations when business transactions are carried out;
- — completeness, reliability, usability and reliability of the Company’s financial, accounting and management information and reporting.
Internal Control Principles
- system approach;
- timeliness;
- unity;
- continuity;
- separation of powers;
- documentation of procedures;
- documentation of results;
- feasibility;
- interaction;
- development.
The principles of internal control disclosed in the 2011 Report have not changed and the Company continues to follow them.
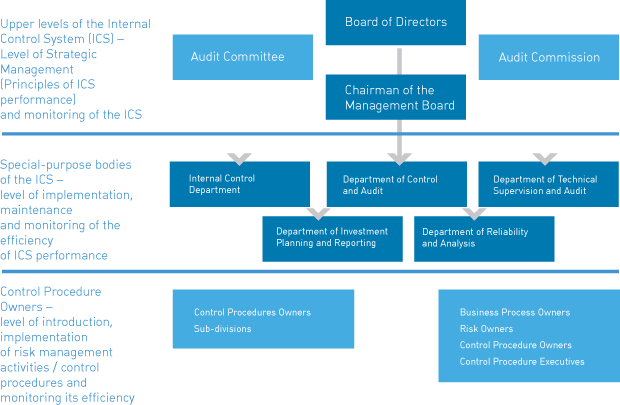
The Structure of the Internal Control System’s Bodies and Communications
The internal control system’s participants are:
- — Board of Directors;
- — Audit Commission;
- — Audit Committee of the Board of Directors;
- — Chairman of the Management Board;
- — special-purpose bodies of the internal control system;
- — the Company’s Internal Units
Further information about the functions of the internal control system bodies is presented in the 2012 Annual Report of Federal Grid Company.
The effectiveness of the internal control system is provided by the interrelation of the three constituents of management processes:
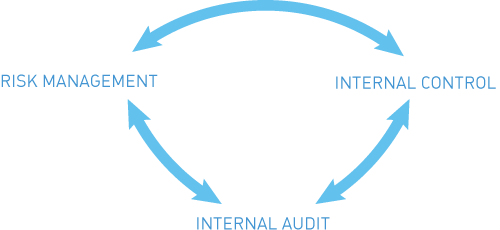
The Company widely uses the practice of conducting comprehensive inspections of its branches and SDCs, in which, along with the specialized control bodies, other departments of Federal Grid Company are involved.
In 2012, specialized control bodies performed inspections in all Federal Grid Company’s branches – Backbone Electric Grids (MES). 21 SDCs of Federal Grid Company were audited.
Subjects of inspections:
- internal audit of business processes;
- technical audit (complex and target audits);
- audit of financial and operating activities;
- audit of facilities’ preparedness to operate in autumn-winter period and in special conditions;
- internal complex and target audits (including investment projects implementation, fulfillment of budgets, programs and plans, execution of agreements etc.).
Based on the inspection results, measures are being taken promptly and in full to address the revealed violations, shortcomings, deviations, with a subsequent control over the implementation of all planned activities.
2013 Plans to Improve the Internal Control
Following the adoption of the revised Regulations on the Internal Control System, development priorities are: implementing standardized approaches to the realization of internal control functions in the branches, updating the similar regulations in subsidiaries and dependent companies, introducing IT-solutions in the area of internal control.
In the first half of 2013, the Company plans to adopt the Strategy of Internal Control System Improvement, which will be implemented in 2013-2014.
The Strategy defines the main goals and directions of development of the internal control system and risk management at all levels (in the head office, branches and SDCs) and in all processes (areas of activities) of the Company.
The following are key objectives of upgrading the Internal Control System:
- — integrating the Internal Control System and risk management into a single management system for the prevention, timely detection and prompt responses to risks and threats;
- — building effective working business processes unified throughout the entire command chain, including the minimum necessary control procedures, which are developed considering implementation costs and its effectiveness;
- — introducing a risk-oriented internal audit, also stipulating the planning of inspection procedures based on risk assessment – to focus on the most vulnerable facilities and activity sectors.

 square km
square km