- Federal Grid Company – Ten-year results
- Operations overview
- Social responsibility and sustainable development
- Financial performance overview
- Corporate governance report
- Share capital
-
APPENDICES
- Information on compliance with the FCSM corporate code of conduct
- Implementation of the assignments of the president and the government of the Russian Federation
- Information on transactions performed by JSC Federal Grid Company in 2012, recognized by russian federation laws as interested party transactions, and which are subject to the approval of the company’s authorized management body
- Audit Commission Conclusion on the Audit of Operational and Financial Activities of Federal Grid Company for 2012
- 2013 investor calendar
Economic aspect
Economic Aspect – Improving Energy Efficiency
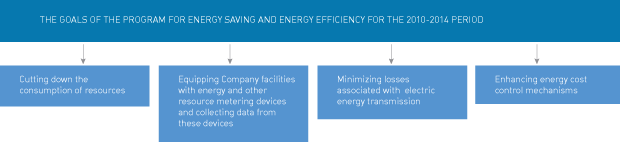
Energy efficiency is one of the priorities of Russia’s technological development. Pursuant to the Russian Federal law “On Energy Saving and Improving Energy Efficiency,” the Company developed a program for energy saving and improving energy efficiency (for the 2010-2014 period). The Program is intended to provide for the economic and rational use of fuel and energy resources by upgrading the energy efficiency of the Company’s equipment and facilities.
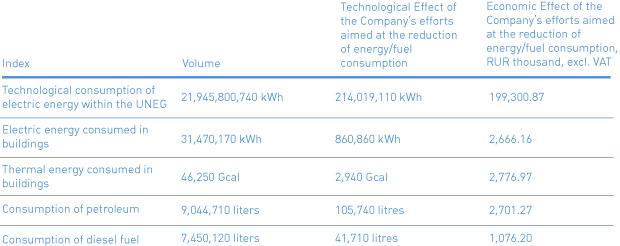
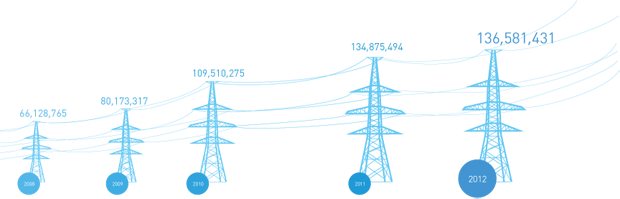
Data on the Volume of Technological Power Consumption in the UNEG and Fuel and Energy Resources Used by the Company
In 2012, fuel and energy resources used by the Company included: electric and heat power, and fuels and lubricants (petroleum and diesel fuel).
Fuel and Energy Consumption Volumes (as accounted for by the Program)
Economic Aspect – Import Substitution
The Company strives to minimize its import dependence by developing the manufacture of electro-technical equipment domestically and by increasing the share of Russian equipment in the Company’s investment program, as well as in repair and targeted programs.
In pursuit of the above-mentioned goal, the Company has signed 95 cooperation agreements, with 77 agreements concluded with manufacturers of electro-technical equipment.
Seventy-two of these are domestic manufacturers. All agreements are intended to facilitate cooperation in the field of development and the use of the most innovative technologies and equipment.
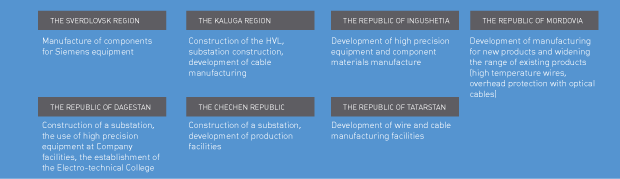
The Company’s cooperation with regional enterprises
The results of the Company’s import substitution initiatives implemented during the reporting year are as follows:
- JSC Elektrozavod launched the manufacture of 100-500 kV transformer equipment, pursuant to a long-term agreement to supply electrical products to the Company’s facilities;
- The 110-500 kV SF6 insulated manufacturing facility was constructed by Hyundai Electrosystems LLC (in the city of Artyom). The supply of SF6 insulated equipment to the Company’s facilities will commence in 2013, pursuant to the long-term agreement for the supply of electrical products, which the Company concluded with Hyundai Electrosystems LLC;
- Izhora Transformers LLC, a company engaged in the construction of a transformer manufacturing facility in Kolpino, was established in cooperation with JSC Power Machines. The manufacture and supply of 110-500 kV transformers will start in 2014;
- The first power and distribution transformers were supplied to the Company’s facilities, pursuant to a supply agreement concluded with JSC Elektrozavod.
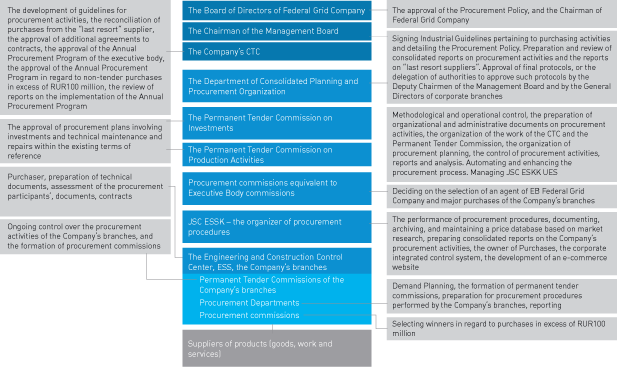
Economic Aspect – Procurement Activities
The Company is actively making purchases in all regions in which the Company operates. The Company’s procurement activities are designed to purchase equipment and services on the competitive market. Procurements are made using funds from the Company’s investment, repair and targeted programs.
The Principles of the Company’s Procurement Activities

The Goals of Procurement Activities

The Procurement System Model
As early as 2008, long before State and municipal orders for open and competitive procedures went electronic, the Company started to implement procurement procedures using an e-commerce system called TZS Electra. Beginning in October 2012, the Company placed its orders on the official all-Russian website www.zakupki.gov.ru. To encourage competition, the Company also approved the use of two more e-commerce websites, www.etp.roseltorg.ru (owned by JSC EETP) and www.sberbank-ast.ru (owned by Sberbank-AST).
The main document regulating the Company’s procurement activities is the Policy on the procedure for the regulated purchases of goods, work and services. The Policy provides for organizing the purchases of goods, work and services based on unified guidelines, using advanced procurement procedures (which are mostly tender-based).
The share of tender-based purchases made by the Company in 2012 was traditionally high, amounting to RUR158,526,746.2 million, or 91% of total corporate procurements.
The Structure of 2011 Regulated Procurements by Type
Economic Aspect — Innovations
The use of innovative technologies in the national economy, including the power industry, is one of the ways to ensure the country’s energy security and sustainable development. Innovations used in the power industry directly influence living standards, driving the development of the country and society as a whole. One of the Company’s priorities involves implementing innovations, as this process is of paramount importance to the economic growth of Russia and its regions.
During the reporting year, the Company proceeded with implementing the Innovative Development Program for the period till 2016, with a view till 2020. Within the framework of the Program, we have made steps to modernize and develop the UNEG, and to form the conceptual, technological and manufacturing basics and terms of development for the smart energy system based on the active adaptive system (SES AAS), to implement pilot projects, and to enhance business processes and organizational mechanisms of the Company to accomplish innovative development tasks.
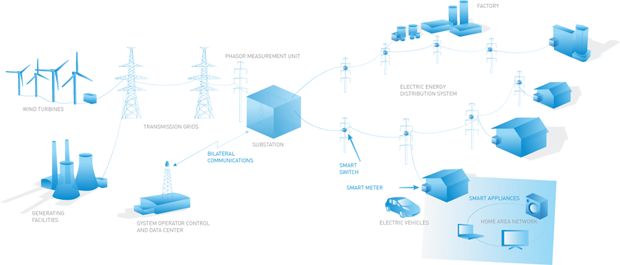
The smart energy system – a new era in the electric energy sector:
Smart grid operation scheme
A smart grid (a part of the active-adaptive grid) uses new principles and technologies for electric energy transmission and conversion which leads to:
- High rate of active elements in the grid, which changes the topological parameters of the grid;
- Large number of sensors measuring current regime parameters to assess the grid’s status in various regimes of energy system operations;
- System of data collection and processing (software and hardware) and a system of active grid elements and consumer electric energy devices management;
- Existence of required executive bodies and mechanisms providing for the on-line adjustment of grid topology changes and allowing for interactions with adjoining energy facilities;
- Tools for the automatic evaluation of the current situation and development forecasts of the grid’s operations, high processing speed of the management system and information exchange.
We are confident that the Company’s Innovative Development Program will contribute to the more efficient use of Russia’s energy potential, providing for the fully-featured integration of UES of Russia into the global energy market, contributing to the development of innovative technologies and ensuring the development of the domestic industry, which will result in all of the positive technological and socio-economic effects listed below:
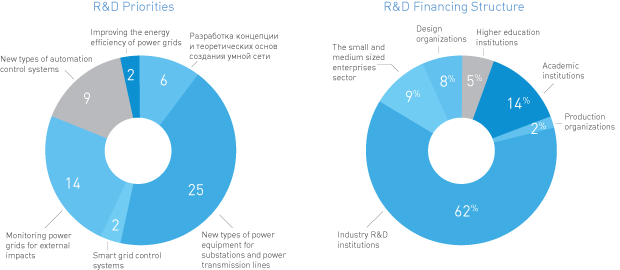
Research and Development (R&D)
The Company’s Innovative Development Program includes performing Research and Development (R&D) work intended to develop, test and implement “breakthrough” and “improving” innovative technologies at UNEG facilities. These technologies include: electric energy storage systems, “digital” substations, high temperature super-conductor technologies and direct current power transmission technologies.
In accordance with the Company’s 2013-2017 Investment Program, in 2012, the Company plans to spend RUR2.9 billion to implement the R&D Program; this is 50% more than in 2011.
R&D Financing Broken Down by Year, RUR billion.
In 2012, our specialists developed and produced more than 10 prototypes for innovative equipment, including:
- A model of a blast resistant transformer (the technology will allow for safe operations of UNEG facilities, to exclude deformation of the transformer with the leaking and ignition of transformer oil and further damage of substation equipment);
- A new type of quick-operating current-limiting 220kV (which allows to limit short circuit currents in the 220kV electric grids);
- A multi-polar multi-pole valve inverter for ice melting at high voltage overhead transmission lines;
- A high-voltage impulse generator.
Within the framework of the R&D Program, in 2012, we received 39 useful model patents (including 6 international ones), 6 patents for invention and 19 certificates for software.
As a part of implementing priority pilot projects in UES of the East (territorial energy clusters), we developed a management system project for four substations of the Elgaugol Cluster, as well as a unique program and method for testing.
We also formed Federal Grid Company’s Architectural Committee under the support of the Russian Academy of Science. The Committee is responsible for the development of smart grid architecture. Among Committee members are representatives of various energy organizations and industry experts.




 square km
square km