The Company’s Impact On Russian Regional Development
Federal Grid operates in 75 Russian regions. We are aware of the Company’s significant role in resolving problems (both economic and social) that are essential for the regions. Thus, we make every effort to enhance our contribution to the regions’ economies, to establish new and to maintain existing employment opportunities, to heighten the education level of people living in the regions and to participate in environmental protection activities.
Social Aspect – Educational Programs
Power engineering is a responsible business and the industry needs highly qualified young specialists. We do everything in our power to train industry professionals in all regions in which the Company operates.
Educational initiatives implemented in 2012 included the following:
- — The traditional annual Day of Federal Grid Company was attended by some 1700 students from regional higher education institutions. Topics discussed with students by Company specialists included: production, corporate culture, and Company-specific operations. The specialists also answered different questions that attendees were interested in;
- — From April to June 2012, the Company hosted a second contest for students and post-graduates from industry higher education institutions to find the best research paper on main power transmission lines. The winners were awarded at the Youth Round Table (which the Company organized in Saint Petersburg);
- — On 18 April 2012, the Company organized an All-Russian Conference entitled “New Generation for the New Power Industry”. The Conference was attended by 300 managers of higher and secondary occupational education institutions from across Russia. The Conference agenda was dedicated to the need to comprehensively modify existing relationships between institutions engaged in educating specialists, and production facilities that are busy with large-scale technical renovation;
- — In 2012, the Company organized excursions to its production facilities for more than 760 students. Nine teachers from higher education institutions underwent production training at the Company’s facilities;
- — On 20 June 2012, a ceremonial opening of the Center for the Advanced Training and Re-training of Power Grid Complex Specialists was held. The Center was organized on the basis of the Saint Petersburg State Polytechnic University, which was equipped and re-constructed with support from the Company;
- — The Company provided charitable assistance to the North Caucasus Federal University to upgrade equipment in the electro-technical laboratory. Similar assistance was provided to the Oil Technical University in Grozny, where the Company has funded the purchase of equipment for the Department of Secondary Occupational Education, namely for classrooms and laboratories that provide education on electric power plants, grids and systems and relay protection and the automation of energy systems, as well as on power supply.
The Company continues to employ the best students from industry education institutions and makes every effort to retain promising young specialists in the Company.
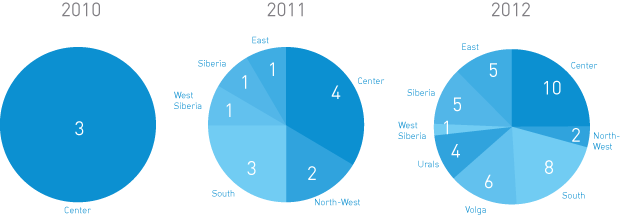
During the reporting year, the Company also moved forward with developing the tradition of having student construction teams work at Company facilities. In July-August 2012, employment was provided for 745 students (twice as many as compared with 2011) from 28 higher and 3 secondary education institutions. They worked at 41 Company facilities under construction. In three years, the geography of facilities using student labor has widened considerably:
Territorial Distribution of the Company’s Facilities Using the Services of Student Construction Teams
The number of students completing practical training at the Company’s facilities grows year-on-year. In 2012, this number stood at more than 720 students.
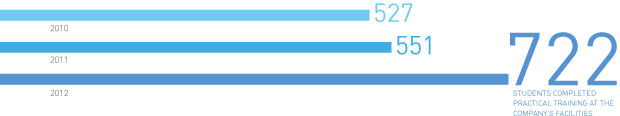
Social Aspect – Charity Projects
The amount spent by the Company to provide aid to physical persons in 2012 comprised RUR3.7 million.
The amount spent on aid projects to organizations during the reporting year stood at RUR138.355 million.
Twenty employees of the Kuban MTPL facility (one of the Company’s branches) who had properties suffered from the Krymsk flood receiv non-repayable subsidies to upgrade their housing conditions. The to amount of non-repayable subsidies comprised RUR24.138 million. Furthermore, Company employees collected RUR5.2 million to aid th people of Krymsk.
Social Aspect – Import Substitution
Localizing the manufacturing of electro-technical equipment on Russian territory will contribute to the domestic economy, thus improving the country’s social situation.
The Company cooperates with leading construction, engineering and other contractor organizations, including: suppliers of highly efficient electro-technical equipment from across the country. The Company signed cooperation agreements with 72 domestic equipment manufacturers. The total number of employees working in these organizations amounts to more than 160 thousand. We are sure that our collaboration will contribute to preserving these jobs, as well as to stimulating the establishment of new job opportunities. According to our estimates, import substitution initiatives will contribute to establishing more than 3000 new jobs in the 2012-2014 period.
Social Aspect – Production Safety
Labor Safety
The Company’s labor safety policy is intended to prevent production accidents and occupational deaths, as well as to provide for the safe behavior of employees engaged in production, to develop accident prevention skills and to ensure improved labor conditions on an ongoing basis.
Based on the analysis of previous performance, we have adjusted labor safety management during the reporting year. In 2012, each PMES implemented procedures to decrease the employee accident rate based on the assessment of safety risks at its facilities, and in compliance with a set of goals formulated by resolutions of the Labor Safety Committee and by the organizational and administrative documents of Federal Grid Company.
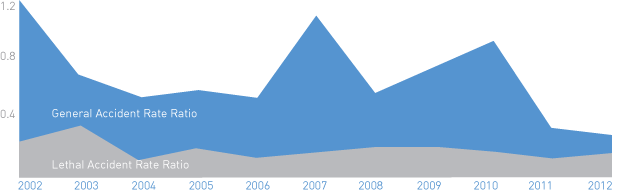
In 2012, the number of accidents fell 14.3% (from 7 to 6 accidents), with the number of injured employees falling 12.5% (from 8 to 7 employees), whereas the number of lethal accidents grew 33% (from 3 to 4 employees). It was the first year in the Company’s ten year history when the accident rate fell (to its minimum).
General and Lethal Accident Rates at the Company’s Facilities
To improve production safety, the Company implements labor safety procedures prior to the start of the repair campaign, assessing employee safety risks and developing corrective actions. The Company also creates instructional films that reflect safe methods of work and controls and analyzes the safe performance of work by repair teams.
In addition, labor safety initiatives implemented during the reporting year have included the following:
- — A project on the use of mobile video recorders to register the most dangerous actions of personnel working at the power plants;
- — A changed focus of Labor Protection Days to increase efficiency and prevent disturbances which can lead to accidents;
- — Organizing the operation of 50 stationary and 17 mobile safety instruction units to promote safe labor conditions and to train personnel on safe methods of work, based on up-to-date requirements;
- — Further operation of 13 psychological rehabilitation units intended for operating personnel at substations;
- — Developing standardized requirements for the certification of workplaces in regard to work conditions and the summing up process, followed by granting benefits and compensation to employees;
- — Further continuation of the “A PMES Best in Labor Safety” and of the “A MES Best in Labor Safety” contests.
Industrial Safety
In 2012, the Company operated 342 Hazardous Production Facilities (HPFs) that were registered in the State Registry. To provide for the safe operation of the HPFs and to prevent accidents and to ensure preparation for the liquidation of said accidents, the Company has implemented the following:
- — Registration/exclusion/re-registration of the HPFs in the State Registry;
- — Development and putting into effect documents that regulate the safe operation of the HPFs;
- — Reception of positive industrial safety expert conclusions concerning emergency localization and liquidation plans and concerning documents related to the transportation of hazardous substances. The conclusions obtained from the Russian Federal Service for Environmental, Technological and Nuclear Supervision are registered under #08-ID-(Ò)1272-2012 and #08-ID-(Ò)1240-2012, respectively;
- — Insurance of general liability against harm done as the result of an accident at the HPFs;
- — Training and certification of personnel on industrial safety.
In 2012, the Company approved Guidelines for the certification of technical equipment used at the Company’s HPFs to regulate the procedures for the certification, diagnostics and expert assessment of said equipment.
Fire Safety
No fires were registered at the Company’s facilities or within the Company’s overhead lines guard zones. The only disturbance involving fire that was registered in 2012 occurred at the Kolpino 330 kV SS. The fire occurred due to the damaged input of the 330 kV automatic transformer, which resulted in the emission and inflammation of transformer oil. Damages resulting from the fire amounted to RUR1.63 million.
The decrease in the number of fires at Company facilities caused by substation equipment disturbances is the result of instituting additional fire safety measures during preparation for the fire hazard period, and also due to implementing the Program to upgrade and enhance fire safety at the UNEG and Federal Grid Company. The RUR1,059.7 million assigned for the above-mentioned purposes for the 2011-2017 period are to be generated by the Company’s economic and investment activities. The considerable growth in fire safety costs is caused by the need to replace worn elements of the main firefighting systems.
